
Malaysia is a multicultural country with a rich culinary culture that encompasses Malay, Chinese, Indian, and international cuisines. With rapid economic development and increasing consumer focus on healthy eating, Malaysia's food and beverage industry has shown strong growth momentum in recent years. According to data from the Department of Statistics Malaysia, the total market size of Malaysia's food and beverage industry reached RM30 billion (approximately USD 7.2 billion) in 2022, and it is expected to grow at an average annual rate of 8% by 2025.
For food ingredient suppliers and traders, Malaysia's food and beverage industry is not only a vast market but also a field full of opportunities. However, as the market continues to expand, competition is becoming increasingly fierce. Suppliers and traders need to deeply understand market trends, consumer demands, and industry challenges to stand out in the competitive landscape.
This guide will provide comprehensive market analysis, trend insights, and practical strategic advice for food ingredient suppliers and traders, helping them seize opportunities and address challenges in Malaysia's food and beverage industry.
1. Market Analysis of Malaysia's Food and Beverage Industry1.1 Number and Scale of Food and Beverage Businesses
According to the latest data, there are approximately 150,000 food and beverage businesses in Malaysia, ranging from street vendors to high - end restaurants. The specific distribution is as follows:
Street Vendors and Stalls: Approximately 100,000, accounting for 67% of the total food and beverage businesses.
Small and Medium - Sized Restaurants: Approximately 40,000, accounting for 27% of the total.
Large Chain Restaurants and High - End Restaurants: Approximately 10,000, accounting for 6% of the total.
Appendix 1: Number and Classification of Food and Beverage Businesses in Malaysia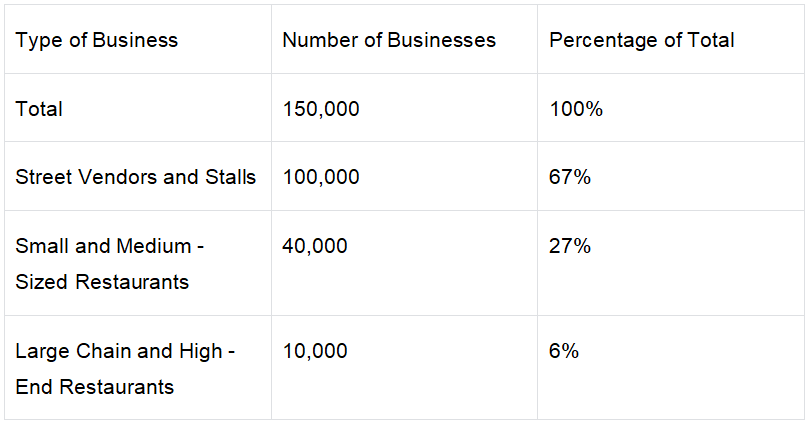
Appendix 2: Scale and Revenue of Food and Beverage Businesses in Malaysia
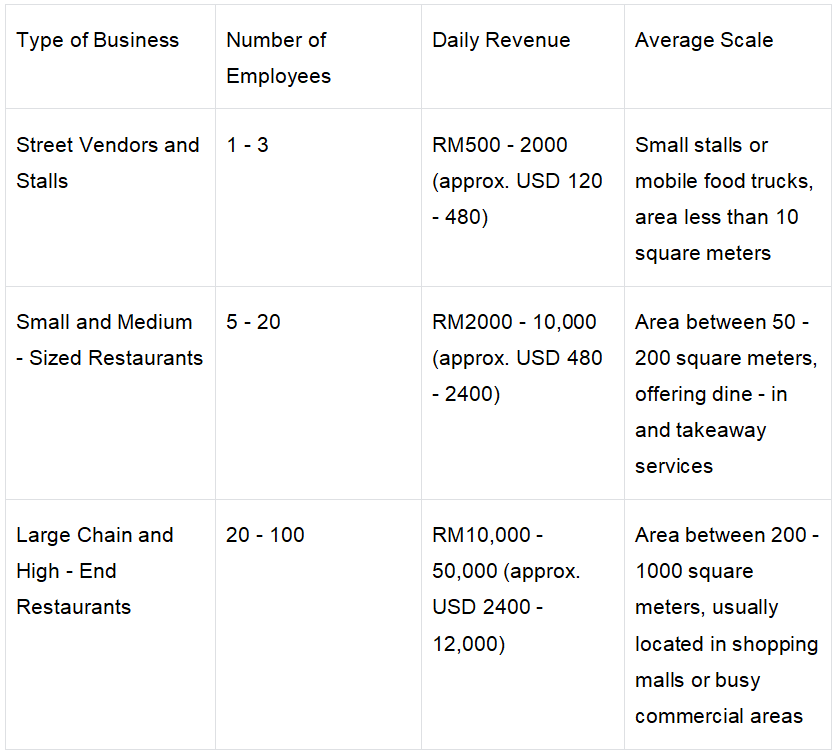
Explanation
Street Vendors and Stalls: Smallest scale, few employees, low daily revenue, typically family - run.
Small and Medium - Sized Restaurants: Medium scale, more employees, higher daily revenue, offering dine - in and takeaway services.
Large Chain and High - End Restaurants: Largest scale, most employees, highest daily revenue, usually located in shopping malls or busy commercial areas.
This list clearly shows the scale, revenue, and operational characteristics of different types of food and beverage businesses in Malaysia, making it easier to understand the industry structure and business models.
1.2 Regional DistributionMalaysia's food and beverage industry is mainly concentrated in the following regions:
Kuala Lumpur: Approximately 30,000 food and beverage businesses, with diverse types of restaurants, mostly small and medium - sized.
Penang: Approximately 15,000 food and beverage businesses, mainly street vendors and small and medium - sized restaurants.
Johor (Johor Bahru): Approximately 12,000 food and beverage businesses, close to Singapore, with a developed food and beverage industry.
Perak: Approximately 10,000 food and beverage businesses, mainly street vendors and small family - run restaurants.
Sabah and Sarawak: Approximately 8,000 food and beverage businesses, mainly local specialty cuisines.
Appendix 3: Regional Distribution of Malaysia's Food and Beverage Industry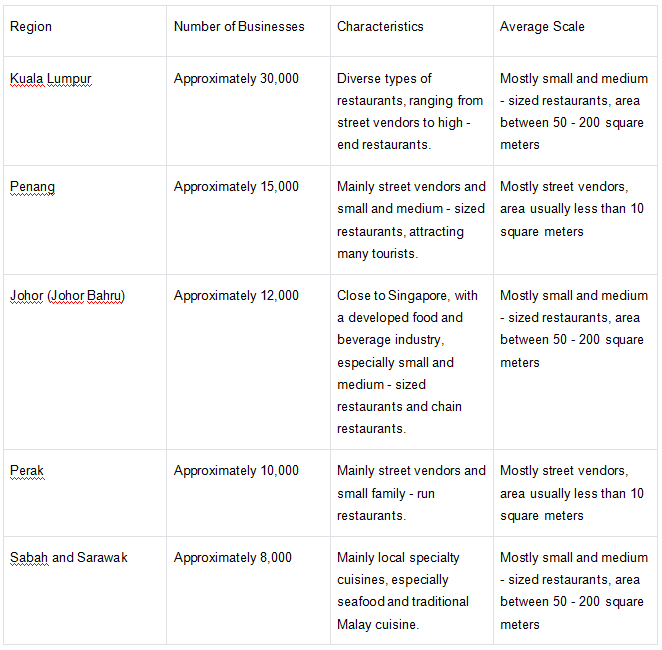
Explanation
Kuala Lumpur: As the capital and economic center of Malaysia, Kuala Lumpur has the most developed food and beverage industry, with diverse types of restaurants, mostly small and medium - sized.
Penang: Mainly street vendors and small and medium - sized restaurants, attracting many tourists, mostly street vendors.
Johor (Johor Bahru): Close to Singapore, with a developed food and beverage industry, especially small and medium - sized restaurants and chain restaurants.
Perak: Mainly street vendors and small family - run restaurants, mostly street vendors.
Sabah and Sarawak: Mainly local specialty cuisines, especially seafood and traditional Malay cuisine, mostly small and medium - sized restaurants.
This list clearly shows the distribution of Malaysia's food and beverage industry across different regions, making it easier to understand the characteristics and scale of the industry in each region.
1.3 Changes in Consumer Demand
In recent years, Malaysian consumers' demand for food and beverages has undergone significant changes:
Healthy Eating: Consumers are increasingly focusing on healthy eating, with growing demand for low - calorie, low - fat, and high - protein ingredients.
Convenience: The rise of food delivery and online ordering services has driven demand for convenient ingredients.
Diverse Choices: Consumers are showing strong interest in diverse and international food options.
2. Trends and Opportunities in Malaysia's Food and Beverage Industry2.1 Healthy Eating Trend
With increasing consumer awareness of health, healthy eating has become an important trend in the food and beverage industry. Suppliers and traders can seize this opportunity by providing the following ingredients:
Organic Ingredients: Demand for organic vegetables, organic mushrooms, and other healthy ingredients is increasing year by year.
Low - Calorie Ingredients: Such as chicken breast, fish, and legumes, which are low in fat and high in protein.
Functional Ingredients: Such as ingredients rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants.
2.2 Rise of Food Delivery and Online Ordering
After the pandemic, food delivery and online ordering services have developed rapidly, becoming an important part of the food and beverage industry. Suppliers and traders can adapt to this trend in the following ways:
Providing Ingredients Suitable for Delivery: Such as ingredients that are easy to package and transport, ensuring freshness during delivery.
Collaborating with Food Delivery Platforms: Partnering with platforms like GrabFood and Foodpanda to expand sales channels. Click here to learn more about the basics of GrabFood, Foodpanda, and other food delivery platforms.
2.3 Sustainability and Environmental Protection
With increasing consumer focus on sustainability and environmental protection, food and beverage businesses are adopting eco - friendly packaging and reducing food waste. Suppliers and traders can meet this demand in the following ways:
Providing Eco - Friendly Packaging: Such as biodegradable packaging materials to reduce plastic use.
Promoting Sustainable Ingredients: Such as locally produced ingredients to reduce carbon footprint.
1. Common Food Delivery Packaging Methods in Malaysia1.1 Plastic Packaging
Characteristics: Plastic packaging is the most common food delivery packaging method in Malaysia due to its low cost, durability, and ease of sealing, widely used in various types of food.
Applications: Commonly used for liquid or semi - solid foods such as soups, rice, and noodles.
Special Features: Some plastic packaging uses leak - proof designs to ensure that soups do not spill, suitable for long - distance delivery.
1.2 Paper Packaging
Characteristics: Paper packaging is environmentally friendly and recyclable, gradually becoming a mainstream choice for food delivery packaging. Paper packaging is typically used for dry foods such as burgers, sandwiches, and pizzas.
Applications: Commonly used in fast food restaurants and Western - style restaurants.
Special Features: Some paper packaging uses waterproof coatings to prevent food grease from penetrating while keeping the packaging clean.
1.3 Aluminum Foil Packaging
Characteristics: Aluminum foil packaging has good insulation properties, suitable for foods that need to maintain temperature, such as grilled meats and fried rice.
Applications: Commonly used for food delivery that requires insulation.
Special Features: Aluminum foil packaging can be directly heated, making it convenient for consumers to heat food at home.
1.4 Biodegradable Packaging
Characteristics: With increasing environmental awareness, biodegradable packaging (such as cornstarch packaging and sugarcane fiber packaging) is becoming popular. This type of packaging can decompose in the natural environment, reducing environmental impact.
Applications: Commonly used in high - end restaurants and health - focused food brands.
Special Features: Biodegradable packaging is not only environmentally friendly but also enhances brand image, attracting environmentally conscious consumers.
2. Special Features of Food Delivery Packaging in Malaysia2.1 Environmental Trends
The Malaysian government and society are increasingly focusing on environmental issues, and many food delivery platforms and food businesses are adopting eco - friendly packaging. For example, GrabFood and Foodpanda have launched "plastic - free packaging" initiatives, encouraging businesses to use biodegradable or recyclable packaging materials.
2.2 Localized Design
Food delivery packaging in Malaysia often incorporates local cultural elements, such as traditional patterns or local languages, to enhance consumers' cultural identity. For example, some packaging features traditional Malaysian patterns or slogans to attract local consumers.
2.3 Multi - Functional Packaging
To enhance the dining experience for consumers, many food delivery packaging designs are multi - functional. For example, some packaging can be folded into placemats for convenient dining, while others are designed as reusable containers to reduce waste.
2.4 Insulation and Leak - Proof Technology
Food delivery packaging in Malaysia has advanced insulation and leak - proof technology. For example, some packaging uses a double - layer design, with an inner layer of aluminum foil and an outer layer of paper material, providing both insulation and leak - proofing. Additionally, some packaging comes with sealing strips to ensure that food does not spill during transportation.
3. Challenges in Malaysia's Food and Beverage Industry3.1 Labor Shortage
Malaysia's food and beverage industry has faced severe labor shortages in recent years, especially for key positions such as chefs and waitstaff. According to data from the Malaysian Food and Beverage Executives Association, the labor shortage in the food and beverage industry reached 15% - 20% in 2022, particularly in major cities like Kuala Lumpur and Penang. The main reasons for the labor shortage include:
Restrictions on Foreign Labor: The Malaysian government has tightened visa and work permit policies for foreign workers, making it difficult for the food and beverage industry to hire enough employees.
Loss of Local Labor: Many local young people are unwilling to work in the food and beverage industry, believing that these jobs are high - intensity, low - paying, and lack career development prospects.
Impact on Food and Beverage Businesses
Labor shortages directly affect the operational efficiency and customer experience of food and beverage businesses. Many restaurants have had to shorten operating hours or reduce service offerings, leading to decreased revenue. Additionally, due to insufficient staff, service quality may also be affected, further impacting customer satisfaction.
Strategies for Suppliers and Traders
To help food and beverage businesses address labor shortages, suppliers and traders can take the following measures:
Providing Semi - Finished Ingredients
Solution: Suppliers can provide semi - finished ingredients, such as pre - cut vegetables, marinated meats, and pre - mixed sauces. These semi - finished ingredients can reduce the reliance on chefs and lower the demand for highly skilled labor.
Data Support: According to a survey by the Malaysian Food and Beverage Executives Association, restaurants using semi - finished ingredients can reduce kitchen labor demand by 20% - 30%.
Promoting Automation Equipment
Solution: Suppliers can promote automated kitchen equipment, such as automatic vegetable cutters, dishwashers, and smart cooking devices. These devices can improve kitchen efficiency and reduce reliance on manual labor.
Data Support: Industry research shows that restaurants introducing automated equipment can reduce labor costs by 15% - 25% while improving production efficiency.
Providing Training Support
Solution: Suppliers can collaborate with food and beverage businesses to provide employee training services, helping existing employees improve their skills and reducing the need for highly skilled labor. For example, suppliers can organize cooking training classes or provide online training resources.
Data Support: According to data from the Malaysian Ministry of Human Resources, employees who have received professional training can improve work efficiency by more than 30%.
Optimizing Supply Chain Management
Solution: Suppliers can optimize supply chain management to reduce inventory pressure and operating costs for food and beverage businesses. For example, suppliers can provide regular delivery services to ensure that food businesses can obtain the necessary ingredients in a timely manner, reducing the need for large inventories.
Data Support: Optimizing supply chain management can help food businesses reduce operating costs by 10% - 15%, freeing up more funds for employee recruitment and training.
3.2 Rising Raw Material Prices
Global supply chain issues and inflation have led to rising raw material prices, especially for imported ingredients. Suppliers and traders can help food businesses reduce costs in the following ways:
Local Sourcing: Promote locally produced ingredients to reduce reliance on imported ingredients.
Bulk Purchase Discounts: Offer bulk purchase discounts to help food businesses reduce procurement costs.
Appendix 4: Malaysia's Major Imported Ingredients in 2023
The following is a summary of data on Malaysia's major imported ingredients in 2023, including ingredient names and import amounts. The data is based on publicly available data from the Ministry of International Trade and Industry (MITI) and the Department of Statistics Malaysia (as of October 2023).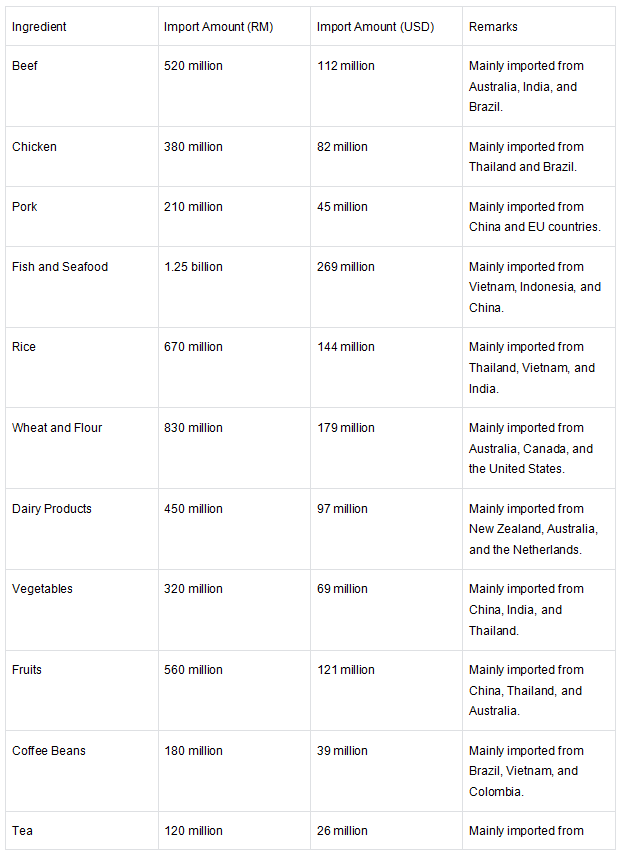
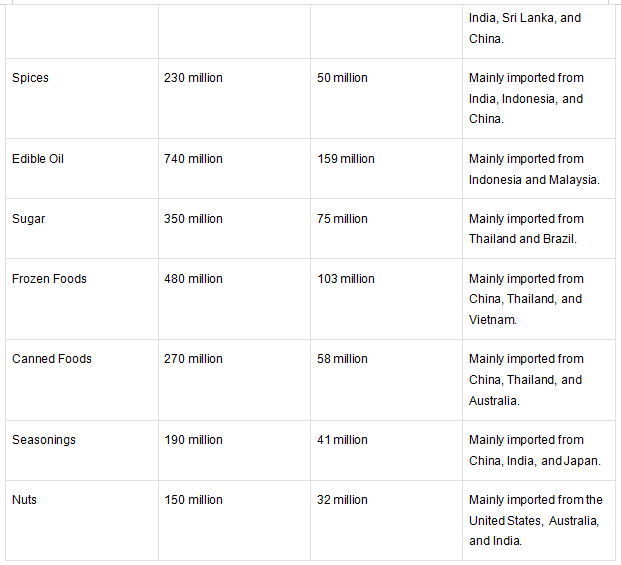
Data Explanation
Beef:





创新博览会LOGO-white.png)


Copyright © China Chamber of Commerce of Food, Native Produce and Animal Products Edible Fungi and Products Branch
京公网安备11010102004652号 京ICP备05021290号-29 | Technical Support: Starify Privacy Policy Sitemap Contact Us
创新博览会LOGO.png)
.webp)
